Search

Search

-Homoarginine_hydrochloride主图.jpg)




-Homoarginine_hydrochloride主图.jpg)




L(+)-Homoarginine hydrochloride is a synthetic, basic amino acid and a stable salt form of homoarginine. It is a homologue of L-arginine, featuring an additional methylene group in its side chain. The "L(+)" denotes its specific stereochemistry, identical to natural proteinogenic amino acids. Primarily used in biochemical research, it acts as an alternative, less efficient substrate and a mild competitive inhibitor for Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS). This allows scientists to modulate and study the nitric oxide signaling pathway in cardiovascular and neurological processes. Its hydrochloride salt enhances stability and solubility for experimental use.
| Items | Specification | Result |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder | White crystalline powder |
| Assay | 98.0%-101.5% | 99.0% |
| Loss on drying | ≤0.2% | 0.1% |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.1% | 0.06% |
| Heavy metals | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 1483-01-8 |
| Appearance: | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Purity: | 98.0%-101.5% |
| MOQ: | 1kg |
| Price: | Negotiable |
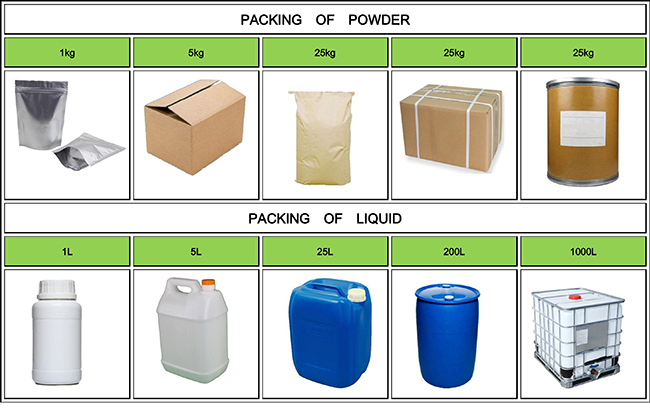
| Package details: | 100g, 1kg/foil bag |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
L(+)-Homoarginine hydrochloride is a chemically modified, salt form of the non-proteinogenic amino acid homoarginine. Its structure and properties are as follows:
Chemical Structure:
Homoarginine: This is a basic amino acid that is structurally analogous to the canonical amino acid L-arginine. The key difference is the addition of a single methylene group (-CH₂-) in its side chain. Specifically, while arginine has a guanidino group attached directly to a carbon chain, homoarginine has the guanidino group attached via an additional -CH₂- unit, effectively making its side chain one carbon longer.
L(+)-: This notation specifies the stereochemistry. The "L" refers to the specific three-dimensional configuration around the chiral alpha-carbon atom, which is the same as that found in the natural, biologically active L-amino acids. The "(+)" indicates that this enantiomer is dextrorotatory, meaning it rotates the plane of plane-polarized light in a clockwise direction.
Hydrochloride (HCl): This indicates the molecule is in a salt form, where the strongly basic guanidino group has been protonated and paired with a chloride counterion (Cl⁻). This form enhances the compound's stability, crystallinity, and solubility in aqueous solutions.
Key Characteristics and Applications:
Biochemical Tool: Homoarginine is not commonly incorporated into proteins during ribosomal synthesis. Instead, it is primarily used as a research tool in biochemical and physiological studies.
Role in Nitric Oxide (NO) Pathway: Its primary significance lies in its interaction with the Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) enzyme family.
It acts as an alternative substrate for NOS. However, it is typically a less efficient or "weaker" substrate compared to its native counterpart, L-arginine.
Because of this, it can function as a mild competitive inhibitor of NOS. By occupying the enzyme's active site, it can reduce the production of Nitric Oxide from L-arginine, allowing researchers to probe the enzyme's function and the role of NO in various processes like vasodilation, neurotransmission, and immune response.
Biomarker Potential: Low levels of endogenous L-homoarginine in plasma have been investigated as a potential biomarker associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality.
In summary, L(+)-Homoarginine hydrochloride is a stable, synthetic amino acid derivative that serves as a crucial pharmacological and research tool for studying the complex roles of the nitric oxide pathway in health and disease.



Guaranteed purity
High quality & competitive price
Quality control
Fast feedback
Prompt shipment

Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 

Prolinol主图.jpg)