Search

Search



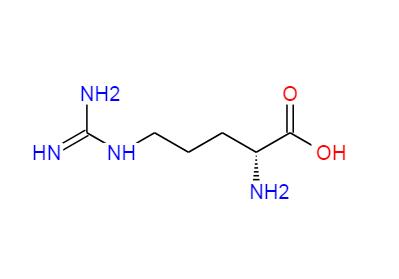
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (often abbreviated as NCGA) is a synthetic analog of the amino acid glutamic acid. It is a derivative where the amino group of the glutamic acid molecule is carbamylated, meaning a carbamyl group (-CONH2) is attached to the nitrogen of the glutamic acid's side chain.
Key points about N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid:
Chemical Structure: It consists of the glutamic acid backbone with an additional carbamyl group attached to the nitrogen in the side chain.
Function and Use:
NCGA is mainly used in scientific research to study the role of glutamate in various biochemical pathways.
It has been explored for its potential use in enhancing the activity of certain enzymes, especially in the context of nitrogen metabolism.
NCGA is also studied for its potential therapeutic effects, particularly in relation to conditions like hyperammonemia, where the body struggles to clear ammonia due to liver dysfunction.
Biological Role: In some biochemical contexts, NCGA can mimic the role of glutamate, influencing pathways related to amino acid metabolism and nitrogen balance.
Research Applications: It has been used in experiments involving metabolic pathways, enzyme activity regulation, and studying diseases related to amino acid metabolism.
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (NCGA) has several applications, primarily in scientific research and potential therapeutic contexts. Below are its main applications:
Clinical Use: NCGA is most notably used in the treatment of hyperammonemia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of ammonia in the blood. This condition often occurs due to liver dysfunction, urea cycle disorders, or other metabolic diseases.
Mechanism: NCGA acts as a surrogate to carbamoyl phosphate, which is involved in the urea cycle (a metabolic pathway that detoxifies ammonia). It helps by facilitating the excretion of excess ammonia in the body, reducing the burden on the liver and kidneys.
Specifically in Urea Cycle Disorders (UCDs): NCGA has been explored for its ability to bypass certain metabolic blockages in the urea cycle, allowing for better detoxification of ammonia in patients with these disorders.
Glutamate and Nitrogen Metabolism: NCGA is a useful tool in studying nitrogen metabolism and glutamate pathways in various organisms. It can be used to study how the body processes nitrogen-containing compounds and the roles of specific enzymes in the urea cycle or amino acid metabolism.
Enzyme Regulation: NCGA can be used to study enzyme activity, particularly in relation to enzymes involved in the urea cycle and glutamate metabolism. By influencing these enzymes, researchers can understand their function and potential for therapeutic targeting.
NCGA has been studied as a precursor or part of therapeutic regimens for conditions related to ammonia detoxification, especially in patients with compromised liver function or metabolic disorders affecting the urea cycle.
Its effects on the glutamate-glutamine cycle may be of interest in neurodegenerative conditions or disorders related to glutamate dysregulation.
In liver diseases, where the ability to detoxify ammonia is impaired, NCGA may help in reducing the toxicity caused by ammonia buildup, thus providing a supportive treatment in conditions like cirrhosis or acute liver failure.
Researchers use NCGA to investigate its effects on metabolic disorders, particularly those involving ammonia metabolism and disorders like urea cycle defects, which cause dangerous accumulation of ammonia in the bloodstream.
Given its effects on ammonia processing, NCGA could potentially have applications in nephrology as well, for patients with kidney diseases where nitrogen metabolism or detoxification is impaired.
While NCGA is not a mainstream medication, its main applications are in clinical management of hyperammonemia, especially in conditions like urea cycle disorders or liver failure. It is also used in biochemical research to study amino acid and nitrogen metabolism, particularly in relation to the urea cycle and glutamate pathways.

Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية