Search

Search











Potassium iodide is colorless or white cubic crystals. Odorless, with a strong bitter and salty taste. Melting point 681 °c, boiling point 1330 °c. Soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone, glycerol and liquid ammonia, slightly soluble in ether. Its aqueous solution is neutral or slightly alkaline. Potassium iodide is mainly used for the prevention and treatment of simple goiter, thyroid storm and preoperative preparation for hyperthyroidism. In recent years, the clinical application of potassium iodide has been expanding, and it is widely used in the treatment of dermatology, ophthalmology, joint inflammation, lead nephropathy and breast hyperplasia, and has achieved satisfactory results.
Potassium iodide is a food iodine enhancer that is allowed to be used. Iodine is one of the essential trace elements of the human body, and the total amount of iodine in a healthy adult body is 20 to 50 mg.
| Items | Specifications | Results | |
| Assay | ≥99.0% | 99.12% | |
| Iodate | Not more than 4 µ g/g | Passes the test | |
| Loss on drying | ≤1.0% | 0.16% | |
| Heavy metals (Pb) | ≤0.001% | <0.001% |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 7681-11-0 |
| Appearance: | White crystalline powder |
| Purity: | 99%min |
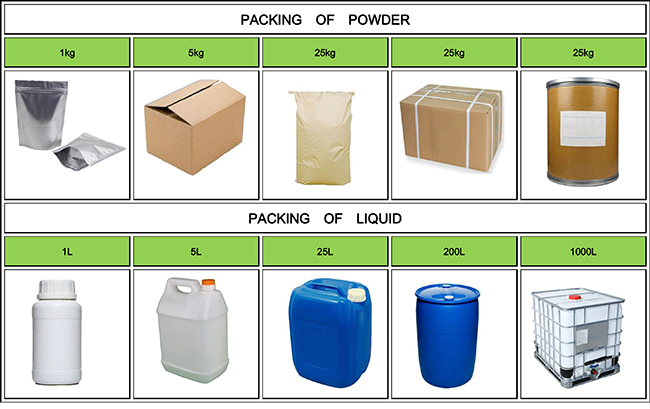
| Package details: | 25kg/drum |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
Potassium iodide (KI) is a white, crystalline salt made up of the elements potassium (K) and iodine (I). It is the most common form of iodine used for nutritional supplementation and medical treatment.
Its chemical formula is simply KI.
It is stable in dry air but can slowly absorb moisture and turn yellow upon long-term exposure to air, as it absorbs carbon dioxide (CO₂) and moisture, causing a small amount of iodine to be released.
Appearance: White, crystalline powder or granules.
Taste: Sharp, bitter, salty taste.
Solubility: It is highly soluble in water. This property is crucial for its use in liquid preparations and for quick absorption by the body.
Potassium iodide has two main categories of use: nutritional/thyroid health and emergency radiation protection.
This is its most common everyday use.
Iodine Source: Iodine is an essential trace element required for the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). These hormones regulate metabolism, growth, development, and body temperature.
Preventing Iodine Deficiency: In areas where the soil is iodine-deficient (leading to low iodine in food), KI is added to table salt ("iodized salt") to prevent iodine deficiency disorders (IDD). These disorders can lead to goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) and severe developmental issues like cretinism in children.
Thyroid Blocking in Medical Procedures: KI tablets are sometimes prescribed before certain medical imaging procedures that use radioactive iodine contrast dyes. By saturating the thyroid with stable (non-radioactive) iodine, the gland is "blocked" from absorbing the radioactive tracer, protecting it from unnecessary radiation exposure.
This is the use KI is most famously known for.
Nuclear Accident Preparedness: In the event of a nuclear reactor accident or detonation of a nuclear weapon, radioactive iodine (Radioiodine, I-131) is a major fission product released into the air.
How it Works: If inhaled or ingested, radioactive iodine (I-131) is concentrated in the thyroid gland, just like stable iodine. This can lead to thyroid cell damage and significantly increase the risk of thyroid cancer years later, especially in children.
KI works by flooding the thyroid with stable, non-radioactive iodine.
This saturation effect "blocks" the thyroid from absorbing and retaining the radioactive I-131.
The radioactive iodine is then largely excreted from the body through urine, preventing long-term harm.
Crucial Timing: For KI to be effective, it must be taken just before or immediately after exposure to radioactive iodine. It is not a general "anti-radiation" pill and offers no protection against other radioactive elements or external radiation exposure. Its protection lasts approximately 24 hours.
Pharmaceuticals: Used as an expectorant in some older cough medicines to loosen mucus in the airways (though this use is less common now).
Chemistry: Used as a source of iodide ions in chemical synthesis and analytical chemistry (e.g., in the "iodine clock reaction").
Photography: Was a key component in photographic developers and fixers in traditional film photography.
Generally Safe: For short-term use at recommended doses, KI is very safe for most people.
Side Effects: Can include skin rashes, salivary gland inflammation, metallic taste, burning in the mouth or throat, upset stomach, and diarrhea.
Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some people can have severe allergic reactions.
Critical Warnings:
Not for Everyone: People with known iodine allergy, certain thyroid conditions (like dermatitis herpetiformis or hypocomplementemic vasculitis), or kidney disease should not take KI without explicit medical direction.
Dosage is Key: The dose is based on age and body size. Taking more than recommended does not offer more protection and increases the risk of side effects.
Not a General Antidote: KI only protects the thyroid from radioactive iodine. It does not protect other parts of the body and provides no protection against other radioactive materials like cesium-137.
Do Not Take Preemptively: KI should only be taken when instructed by public health officials during a confirmed radiation emergency involving the release of radioactive iodine. Stockpiling and self-administering without cause is not recommended.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | A salt composed of potassium and iodine (KI). |
| Primary Functions | 1. Nutrition: Prevents iodine deficiency (via iodized salt). 2. Emergency Medicine: Protects the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine in a nuclear incident. |
| Mechanism of Action | "Thyroid Saturation" - Floods the thyroid with stable iodine, blocking the uptake of radioactive iodine (I-131). |
| Key Limitation | Only protects the thyroid. It is not a general-purpose anti-radiation treatment. |
| Crucial Factor | Timing. Must be taken immediately before or right after exposure to be effective. |
In essence, potassium iodide is a simple compound with a life-saving purpose. It is a critical public health tool for preventing thyroid cancer in populations exposed to one specific and dangerous byproduct of nuclear fallout.




Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية