Search

Search

Introduction to Rifaximin
Rifaximin, CAS 80621-81-4, is a semi-synthetic antibiotic derived from rifamycin, a compound originally isolated from the bacterium Amycolatopsis mediterranei. It is primarily used to treat gastrointestinal conditions due to its unique pharmacokinetic properties, which allow it to act locally within the gut without significant systemic absorption. This characteristic makes Rifaximin particularly effective for treating conditions like traveler’s diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) with diarrhea, and hepatic encephalopathy. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other regulatory bodies worldwide, Rifaximin has become a cornerstone in the management of these conditions.
Uses and Market of Rifaximin
Rifaximin’s primary use is in the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea caused by non-invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Its efficacy in this area has been well-documented, making it a popular choice for travelers to regions where such infections are common. Another significant application of Rifaximin is in the management of hepatic encephalopathy, a severe complication of liver disease characterized by confusion, altered level of consciousness, and even coma. By reducing the production of ammonia and other toxins by gut bacteria, Rifaximin helps to prevent the recurrence of this debilitating condition.
In recent years, Rifaximin has also gained traction in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D). Clinical trials have shown that Rifaximin can significantly reduce symptoms like abdominal pain and stool frequency, providing much-needed relief for patients who often have limited treatment options.
The market for Rifaximin has expanded considerably since its initial approval. According to market research, the global Rifaximin market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7% over the next decade. This growth is driven by increasing awareness of gastrointestinal disorders, rising prevalence of liver diseases, and the expanding indications for Rifaximin use. Major pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in research and development to explore new therapeutic applications for this versatile antibiotic.
Rifaximin vs. Rifampin:
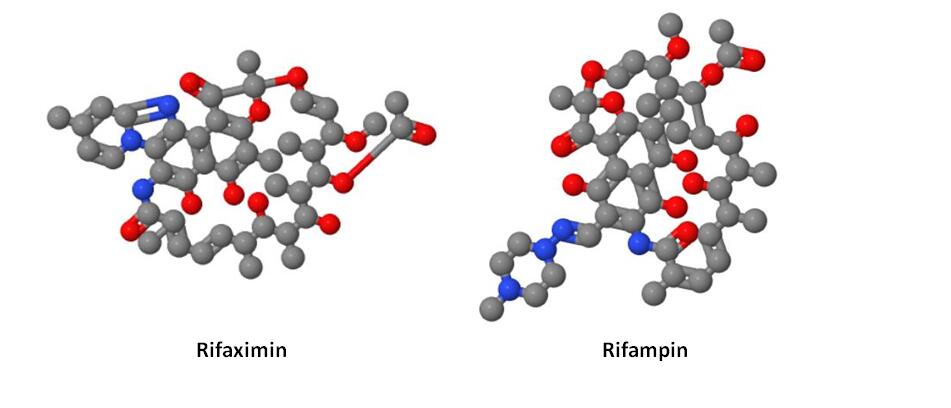
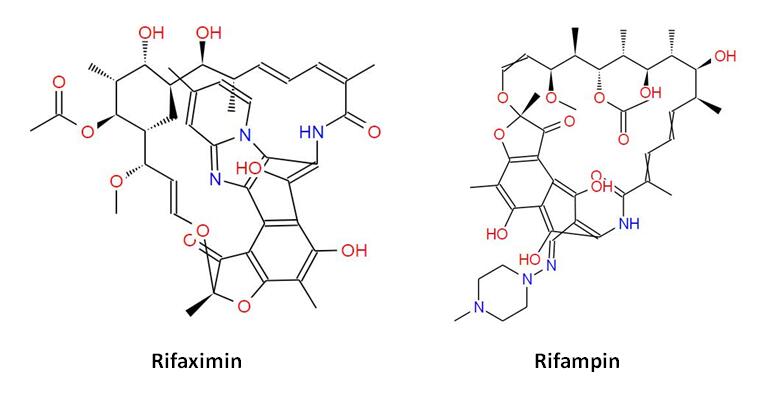
Rifaximin and Rifampin are both antibiotics derived from rifamycin, but they have distinct differences in their pharmacokinetics, spectrum of activity, and clinical applications. Rifampin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic commonly used to treat tuberculosis and other bacterial infections. It is well-absorbed systemically and can penetrate various tissues, making it effective against a wide range of pathogens. However, this systemic absorption also leads to a higher risk of side effects, including hepatotoxicity and drug interactions.
In contrast, Rifaximin is minimally absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, which limits its action to the gut. This localized effect is advantageous for several reasons:
Reduced Systemic Side Effects: Because Rifaximin remains largely confined to the gut, it has a much lower risk of systemic side effects compared to Rifampin. This makes it a safer option for long-term use, particularly in chronic conditions like IBS-D and hepatic encephalopathy.
Lower Risk of Drug Interactions: Rifaximin’s minimal systemic absorption also means it has fewer interactions with other medications. This is particularly important for patients with complex medical histories who may be taking multiple drugs.
Targeted Action: Rifaximin’s localized effect in the gut allows for a high concentration of the drug at the site of infection or inflammation. This targeted action enhances its efficacy in treating gastrointestinal conditions without affecting beneficial gut flora significantly.
Resistance Profile: While antibiotic resistance is a concern for all antimicrobial agents, Rifaximin’s unique mechanism of action and localized effect reduce the likelihood of developing resistance compared to systemic antibiotics like Rifampin.

Conclusion
Rifaximin is a unique and versatile antibiotic with a range of applications primarily focused on gastrointestinal conditions. Its minimal systemic absorption makes it a safer and more targeted option compared to other antibiotics like Rifampin. The expanding market for Rifaximin reflects its growing importance in the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea, hepatic encephalopathy, and IBS-D. As research continues to uncover new therapeutic uses for Rifaximin, its role in modern medicine is likely to become even more significant. With its favorable safety profile and targeted action, Rifaximin stands out as a valuable tool in the management of various gastrointestinal disorders, offering hope and relief to millions of patients worldwide.
Wuhan Fortuna Chemical Co.,Ltd is a professional manufacturer which provide Rifaximin with good quality and best price, welcome to contact us to get COA/TDS/MSDS of Rifaximin.

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية