Search

Search

Understanding Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate
_Gluconate_Dihydrate_3.jpg)
Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate, CAS 59625-89-7, is a chemical compound that serves as a dietary supplement and a source of manganese, an essential trace mineral. Chemically, it is the manganese salt of gluconic acid, and it typically appears as a light pink to pale yellow powder. The “dihydrate” part of its name indicates that each molecule of manganese gluconate is associated with two molecules of water. This compound is often used in nutritional supplements to address manganese deficiencies in the human body.
The Application of Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate
Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate finds its primary application in the field of dietary supplementation. Manganese is a crucial element for human health, playing a vital role in various physiological processes. It is a cofactor for several enzymes, including those involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, and cholesterol. Additionally, manganese is essential for bone formation, blood clotting, and the functioning of the immune system.
In the realm of dietary supplements, Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate is often included in multivitamin and mineral formulations. It is particularly beneficial for individuals who may not obtain sufficient manganese from their diet alone. This can include people with specific dietary restrictions, those with certain medical conditions, or individuals living in areas where the soil is deficient in manganese, leading to lower levels in locally grown food.

Beyond its use in supplements, Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate is also employed in the food and beverage industry as a nutrient fortifier. It can be added to foods and drinks to enhance their nutritional value, ensuring that consumers receive an adequate intake of manganese. Additionally, it is used in animal feed to promote the health and growth of livestock.

Benefits of Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate
The benefits of Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate are primarily linked to its role as a source of manganese. Ensuring an adequate intake of manganese is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Some of the key benefits include:
Bone Health: Manganese is vital for the formation and maintenance of healthy bones. It is involved in the synthesis of bone matrix proteins and the regulation of bone mineralization. Adequate manganese intake can help prevent bone-related disorders such as osteoporosis.
Antioxidant Defense: Manganese is a component of the enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD), which plays a critical role in protecting cells from oxidative damage. By neutralizing free radicals, SOD helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases and supports overall cellular health.
Metabolic Support: Manganese is a cofactor for enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It aids in the conversion of food into energy and supports various metabolic processes, contributing to overall energy levels and metabolic efficiency.
Wound Healing: Manganese is involved in the production of collagen, a protein that is essential for wound healing and tissue repair. Adequate manganese levels can promote faster and more effective healing of injuries.
Neurological Health: Manganese is necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system. It supports the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the regulation of nerve cell function, contributing to cognitive health and neurological well-being.
Comparing Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate and Manganese Bisglycinate
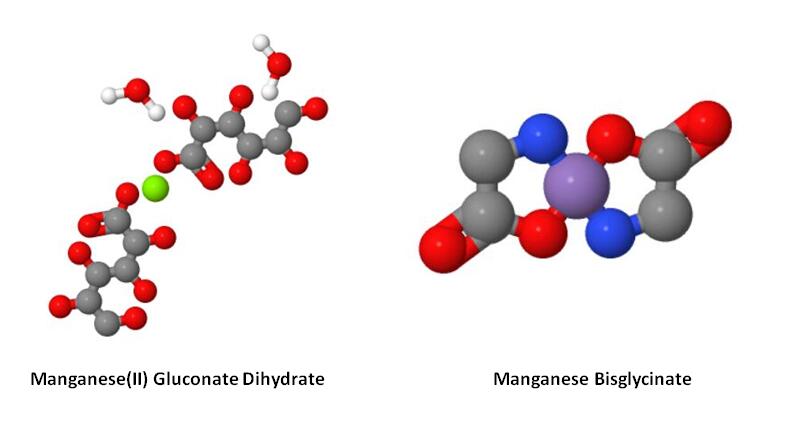
When considering manganese supplements, two common forms are Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate and manganese bisglycinate. Both compounds serve as sources of manganese, but they differ in their chemical structure, absorption, and potential benefits.
Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate is an inorganic salt of manganese and gluconic acid. It is known for its good solubility in water, which can facilitate its absorption in the digestive tract. This form of manganese is widely used in dietary supplements and is generally well-tolerated by most individuals.
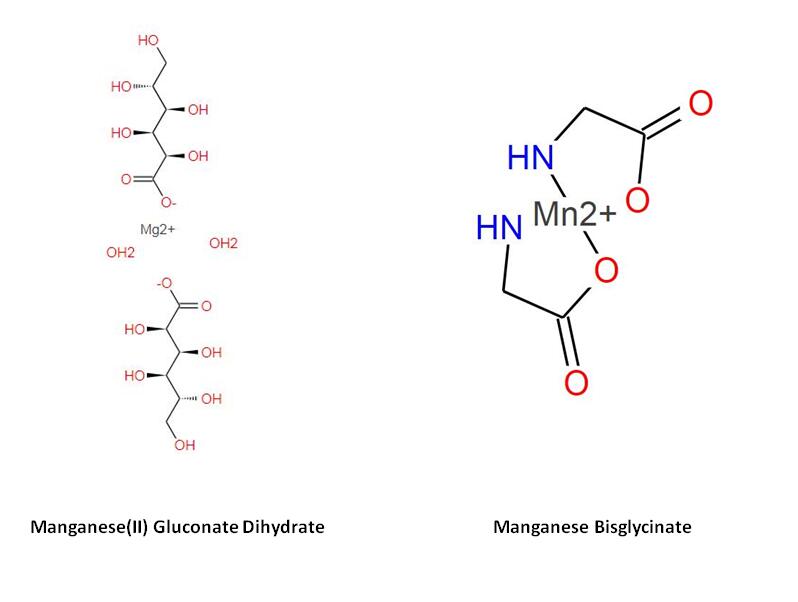
On the other hand, manganese bisglycinate is an organic chelate, where manganese is bound to two molecules of the amino acid glycine. This chelated form is often marketed for its enhanced bioavailability, meaning that it may be more efficiently absorbed and utilized by the body compared to inorganic forms. The chelation process can also reduce the likelihood of gastrointestinal discomfort, making manganese bisglycinate a preferred option for individuals with sensitive digestive systems.
In summary, both Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate and manganese bisglycinate are effective sources of manganese, each with its own advantages. Manganese(II) Gluconate Dihydrate is a reliable and widely used form, while manganese bisglycinate offers potential benefits in terms of absorption and tolerance. The choice between the two may depend on individual health needs, preferences, and specific recommendation.

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية